Guide to Surfacing ‘Unknowns’ for Gigamon Users
The purpose of this blog is to advise our customers how to use the Gigamon Visibility and Analytics Fabric™ (VAF) to identify and strengthen their networks against various exploits. There is intrinsic value in surfacing “unknowns” (test/dev instances, shadow IT, complex multi-IT org situations, etc.) in your environment. The methodology we outline here can be applied to a variety of scenarios or use cases.
Use Gigamon to Help Monitor for Threats
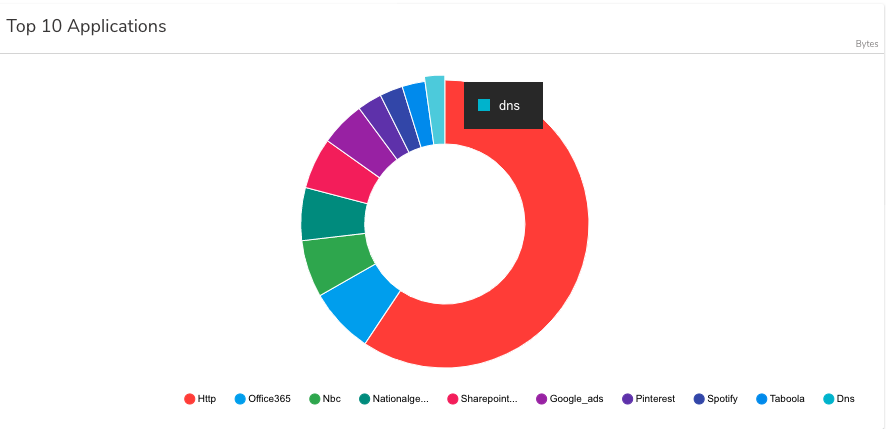
Malware is often characterized and activated by the DNS queries to reach its command and control (C2) server. As a general rule, DNS traffic should be monitored 24/7, with IT continually checking for bad actors and malware behavior. Gigamon customers who have deployed the VAF can isolate all DNS traffic and forward these flows to security monitoring applications or tools by following these best practice steps.
If You Have a Gigamon VAF Visibility Node Without a GigaSMART® Engine:
- Isolate the DNS flows by defining a flow map using a filter for Layer 4 port numbers 53 (DNS over UDP or TCP), 853 (DNS over TLS) and 443 (DNS over HTTPS)
- Specify the destination tool ports as part of the map
Note:
- You should check on the port numbers used by DNS servers on your network in case non-standard ports are being used
- If you know what the IP addresses or subnets are for the management ports of your devices on the network, you can include these as part of the flow map
If You Have a Gigamon VAF Visibility Node With a GigaSMART Engine:
- Create flow maps based on IP addresses or subnets for the management ports of your devices on the network to narrow down the traffic from the network.
- Make sure to include TLS Decryption in your flow map, before the next steps, if DNS over TLS or DNS over HTTPS are in use on your network.
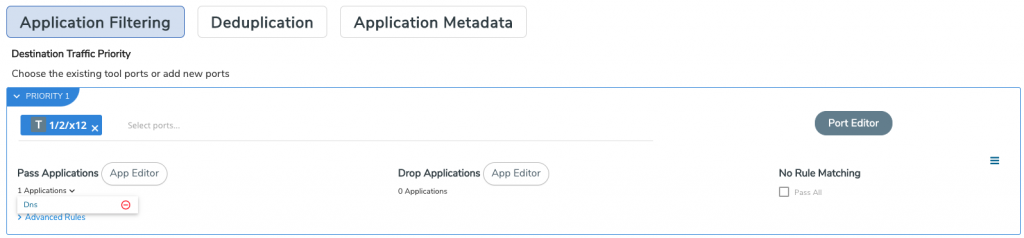
- Use Flow Mapping® to pass the traffic through Application Filtering Intelligence (AFI) so as to forward only DNS traffic to a tool that processes the raw packets. This will correctly identify and isolate the DNS traffic using deep packet inspection and heuristics, regardless of port number used.
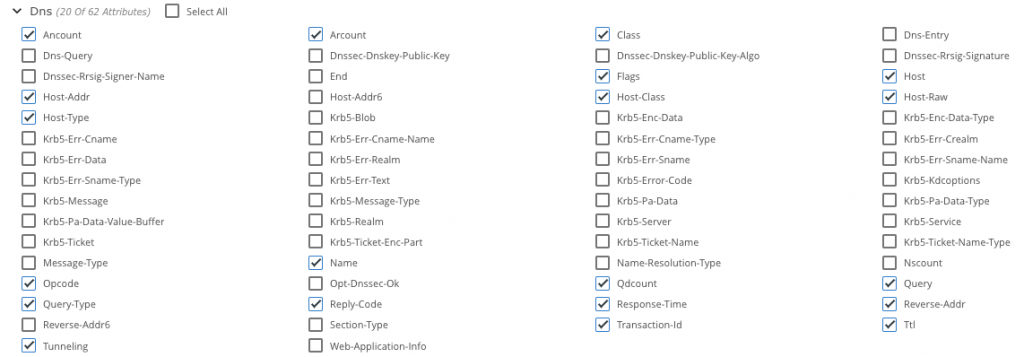
- Use Flow Mapping to pass the traffic through Application Metadata Intelligence (AMI) so as to extract and export DNS metadata and send to a SIEM tool for further inspection (for example, domain names not generated by humans).
- Consider using GigaVUE-FM fabric manager’s API capabilities to communicate with tools in order to adjust any flows. You can go as far as blocking the traffic if the Gigamon solution is deployed inline. For example, users can apply inline drop rules for specific IP addresses.
Featured Webinars
Hear from our experts on the latest trends and best practices to optimize your network visibility and analysis.

CONTINUE THE DISCUSSION
People are talking about this in the Gigamon Community’s Security group.
Share your thoughts today