Operational Technology (OT) Security Explained
Everyone has heard of IT. But what is OT?
OT stands for operational technology, and it plays an important role in a variety of companies and industries worldwide.
In this article, we’ll get into what OT security is, its relationship with IT, and the common problems people who work with OT experience.
What Is Operational Technology (OT) Security?
Operational technology (OT) is any hardware or software used to detect or cause a change in a system via direct monitoring. This may be sensors that keep a server room at a specific temperature or some sort of filtration system that purifies water. It may even look like the automatic regulation of electricity in a power plant or the starting and stopping of traffic lights.
Essentially, operational technology is a physical device that runs on a specific kind of software handling the specific processes and events in a specific location or system.
What Is OT Security?
Even small alterations to the work of OT systems can create massive problems for large numbers of people. OT cyber security, a branch of work in the tech industry, has evolved out of a response to past tampering and a need to stop future problems before they begin.
Common Forms of OT Security: SCADA and ICS
SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) systems are one of the most common forms of OT security used for industrial control systems (ICS). Industrial control systems help manage every aspect of human life from power usage to natural disaster monitoring and beyond.
Because these operational technology systems help control and manage many different and important elements of our personal and professional lives, it’s important to protect them from damage and tampering.
The Relationship Between IT and OT
IT and OT often work hand in hand to accomplish specific tasks. But there are still some differences between the two fields. Here are some of the primary differences between IT and OT that help demonstrate that relationship.
Enterprise vs. Industry
One of the main differences between IT and OT is how the technologies are used.
IT technologies are fairly universal from industry to industry. You’ve got computers, mouses, printers, protocols (like HTTP, SSH, and RDP), and other elements of the IT network. If you work in IT for one industry, you can move to another fairly easily, as the technologies you use are largely the same. In other words, IT deals with universal enterprise software that can be used in a variety of situations.
In OT, however, that’s not the case. OT uses technologies that are very specific to the industry. For example, a lot of OT operates in specific environments under specific situations. It may not have a screen to interact with. It’s not nearly as easy to jump from one industry to another, as the technology is so unique. Whereas IT is enterprise focused, OT is very industry specific.
IT Prioritizes Confidentiality, OT Focuses on Safety
Oftentimes information technology is focused on either storing, retrieving, manipulating, or transmitting information and data in one way or another. So IT focuses on keeping that information secure so only the right people can access, analyze, and manipulate it.
Operational technology, on the other hand, focuses more on safety. One OT device may be tasked with maintaining an exact temperature in a server room so the servers and other tech equipment don’t overheat and break down. Because of that, people who work with OT are more concerned about whether their technology is doing its job keeping environments safe, rather than keeping data secure.
IT Incidents Are More Frequent, OT Incidents Are More Destructive
A lot of things can go wrong when technology is involved. It’s possible to break a system simply by using it incorrectly. Maybe you accidentally uploaded a corrupted file unknowingly. Or maybe someone with malicious intent has tried to hack into your system to either steal your data or just to see if they could.
Whatever the reason, technological problems happen. That said, these problems affect IT and OT differently.
For example, IT tends to have more touchpoints with the internet than OT. That means there’s a far greater chance of an IT-related hack than an OT-related hack. This is why most of the stories that make the news are about stolen data and not destroyed systems. IT problems occur in far greater numbers.
That being said, if something goes wrong with operational technology, it’s more likely to have devastating consequences. Leaked data can be partially fixed by changing passwords, data recovery, and client contact, but an OT problem can have very real consequences in the physical world. Think about an OT system that helps purify drinking water. What are the consequences if the system doesn’t realize that the water it’s sending to people’s faucets isn’t actually clean? How do those consequences compare to the consequences of a password leak?
Security Patching: Every Week vs. Every Ten Years
Lastly, IT moves and innovates at a rapid speed. New patches come out almost every week depending on the specific services you’re using. There’s even a name for it: Patch Tuesday.
That’s fine, as most IT work can be done concurrently while the patch is being applied — but that’s not the case with operational technology.
In OT, you have to shut an entire system down in order to install a patch. So out of necessity, patches don’t come out as frequently for OT systems as they do for IT systems. That’s why operational technology processes seem to lag behind other forms of tech. They can’t just release patches as quickly or as easily.
Why Is OT Security Needed?
So, why is OT security so important?
Operational technology, like all tech, continues to change. Due to the nature of OT, it changes at a slower rate, but nonetheless, innovation is always happening in the OT space. More and more OT systems are finding elements of the work they do online. And the more they appear connected to other networks, the more risk there is that something could go wrong.
OT security continues to grow in importance and will only become more important as software and the means of doing OT work continue to change.
Common Challenges in OT Security
There are some very real challenges when working with operational technology. Some of the most commonly talked about challenges are:
- Lack of awareness regarding OT security issues
- Lack of OT system visibility
- Shared network infrastructure
- Difficulty patching OT
- OT/IT convergence creating more opportunities for security risks
- Remote maintenance often happens over an internet connection
- Third-party access issues
- Not all company locations use the same OT systems
These problems are handled differently from industry to industry. But as technology continues to change, it’s important that those who work with operational technology seek out solutions to these kinds of problems.
Conclusion
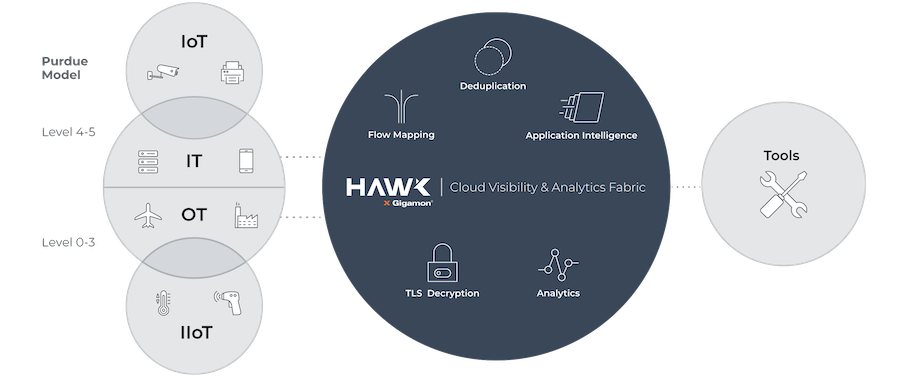
Whether your data comes from information technology or operational technology solutions, you have valuable data that you need to manage. Gigamon helps you do that by providing you and your company with complete cloud visibility.
That means there are no gaps.
Gigamon can help you simplify and secure your hybrid networks, allowing you to take full advantage of the data you own.
Featured Webinars
Hear from our experts on the latest trends and best practices to optimize your network visibility and analysis.

CONTINUE THE DISCUSSION
People are talking about this in the Gigamon Community’s Hybrid/Public Cloud group.
Share your thoughts today







 Dan Daniels
Dan Daniels