What Is Private Cloud?
The cloud has become an essential platform for modern businesses of all sizes. According to the International Data Group, 73 percent1 of organizations have at least one application in the cloud, with an additional 17 percent planning to migrate within the near future.
It should come as no surprise that the cloud industry is growing quickly; Forbes reports that sales for public cloud services revenue alone are projected to reach $411 billion by 2020.2 Cloud provides broad access, infrastructure automation and unsurpassed elasticity, often for a cheaper price — and businesses want in.
What is the difference: Private Cloud vs Public Cloud?
That said, if you’re considering cloud technology for your organization, you should know that not all cloud technology is created equal. Although public cloud is popular, the private cloud sector is growing. Tool suites from private cloud vendors such as VMware and Nutanix and open-source solutions based on OpenStack are gaining adoption. So let’s take a moment and consider public cloud and private cloud.

What Is Public Cloud?
With public cloud, customers work with a third-party provider who manages the service. Authorized users can access cloud-based information and software directly over the internet via self-service portals, often using standard web browsers. One of the key advantages is that the public cloud company oversees the infrastructure, including servers, networking, databases and storage along with the tools to automate the entire platform. They also provide security of the cloud, meaning all the aforementioned components.
Customers don’t have to deal with management and upkeep. Because of this, it is often much easier for a growing business to expand their public cloud usage. Third-party companies already have the hardware resources necessary to sustain growth.
Public cloud typically works on operational costs, meaning clients only pay for the amount of resources they’re using. This means fewer upfront expenses — customers don’t have to invest in hardware — and makes it easier to scale later on.

Of course, one of the downsides with public cloud is that at the end of the day, it is still public, which means multiple cloud tenants are stored on the same hardware. Now, many public cloud companies work hard to provide solid security, but much of this responsibility comes down to the customer. Organizations must provide the security for their applications, identity and access management, operating systems, network and firewall configurations and client/server side data encryption.
What Is Private Cloud?
So, what is a private cloud technology? To answer this question, let’s first address a common private cloud misconception. Many assume that “private cloud” means the hardware is kept onsite and built by the organization itself, but this is not necessarily the case. The datacenter resources may be located on-premises or hosted by a third-party vendor offsite.
The defining difference between public and private cloud isn’t where the hardware is stored, or even who is overseeing said hardware, but what is stored on it. Private cloud users have a dedicated cloud environment for their own use — a single user per cloud, rather than several. The computing resources are isolated and delivered via a secure private network, and not shared with other customers. Private cloud is customizable to meet the unique business and security needs of the organization.

With visibility and management over their private cloud infrastructure, organizations can ensure complete security — both of the core infrastructure as well as everything else, including apps, data and access. For operations involving compliance-sensitive IT workloads and regulatory mandates, IT need not make any compromises on security.
Better yet, private cloud infrastructures often involve fully virtualized environments with automation tool suites to enable an agile software-defined data center. At the same time, the data center enjoys complete control, including access to all packet and application flows, NetFlow generation, high-performance cryptography with latest cipher support and potentially advanced app aware metadata not available in the public cloud.
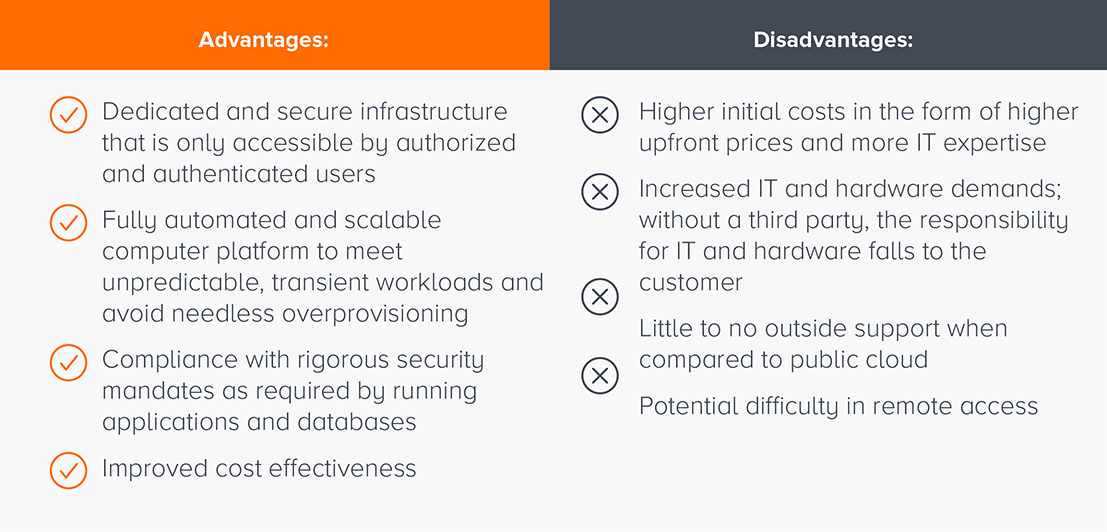
What are the benefits of private cloud?
- Dedicated and secure infrastructure that is only accessible by authorized and authenticated users
- Fully automated and scalable computer platform to meet unpredictable, transient workloads and avoid needless overprovisioning
- Compliance with rigorous security mandates as required by running applications and databases
- Improved cost effectiveness
What are the disadvantages of private cloud?
- Higher initial costs in the form of higher upfront prices and more IT expertise
- Increased IT and hardware demands; without a third party, the responsibility for IT and hardware falls to the customer
- Little to no outside support when compared to public cloud
- Potential difficulty in remote access
Who Uses Private Cloud Infrastructure?
Private cloud is valuable for highly regulated industries and government agencies that rely on keeping sensitive records protected, such as those in the medical field. Similarly, technology companies that require strong control and security over their IT workloads and the underlying infrastructure can benefit from having a private cloud. In fact, some groups, like the aforementioned medical organizations, are required to have a private cloud, rather than public. Still, there are more reasons beyond privacy that explain why a growing number of businesses have adopted the private cloud model.
Larger enterprises and internet of things (IoT) companies that can afford to invest in high performance and available technologies might consider deploying or migrating to private cloud technology as a way to safely handle complex IT needs — especially those that require automated data center designs to operate efficiently and cost-effectively. The heavier the server and network processing load, the more private clouds should be considered. Utilizing the private cloud also gives companies more control over their systems, so for companies that want more independence, the private cloud is a better option. Finally, when discussing the benefits of private cloud, 53 percent3 of surveyed individuals reported that they found the system to be more cost effective than public cloud.

Gigamon Security and Networking for Private Clouds
Visibility is vitally important for ensuring cloud security and optimizing network performance, and Gigamon, a leader in visibility solutions, has a number of platforms to ensure your private cloud is at its safest, with the best end-user experience with the necessary automation support.
For example, Gigamon has teamed up with VMware, which specializes in network virtualization, to provide a two pronged defense for customers. Furthermore, Gigamon has created a product suite for OpenStack for those integrating open-source programming into their private cloud to tackle the unique problems that can arise with this combination, as well as the GigaVUE® Cloud Suite for Kubernetes, which provides visibility into Docker containers managed by Kubernetes.
Gigamon also offers options for public and hybrid cloud security. For those interested in cloud technology, there are many factors to consider. How much computer power are you utilizing? How much money can you afford to spend upfront? How secure does your network need to be? What level of IT expertise do you possess? Choosing cloud technology might be daunting, but the advantages it offers may just make it the right option for your organization.
References
- IDG. “2018 Cloud Computing Survey” IDG. August 14, 2018. https://www.idg.com/tools-for-marketers/2018-cloud-computing-survey/.
- Columbus, Louis. “Cloud Computing Market Projected To Reach $411B By 2020.” Forbes. Forbes Magazine. November 20, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2017/10/18/cloud-computing-market-projected-to-reach-411b-by-2020/#79088a1878f2.
- 451 Research. “Can private cloud be cheaper than public cloud?” VMware. June 2017. https://www.vmware.com/content/dam/digitalmarketing/vmware/en/pdf/products/vrealize-suite/vmware-paper1-can-private-cloud-be-cheaper-than-public-cloud.pdf.
Featured Webinars
Hear from our experts on the latest trends and best practices to optimize your network visibility and analysis.

CONTINUE THE DISCUSSION
People are talking about this in the Gigamon Community’s Hybrid/Public Cloud group.
Share your thoughts today







 Dan Daniels
Dan Daniels