What Is Network Infrastructure?
Updated July 10, 2025.
Network infrastructure refers to all of the resources of a network that make network or internet connectivity, management, business operations, and communication possible.
Network infrastructure comprises hardware and software, systems and devices, and it enables computing and communication between users, services, applications, and processes. Anything involved in the network, from servers to wireless routers, comes together to make up a system’s network infrastructure. Network infrastructure allows for effective communication and service between users, applications, services, devices, and so forth.
The individual components of network infrastructure include:
- Networking hardware devices: Routers, switches, hubs, gateways, bridges, network interface cards (NICs), and modems
- Software network resources: Security applications and access control (NAC) software
- Monitoring and management tools: Network monitoring tools and network management tools
- Network services: Private data center services, virtual network services, and cloud connectivity services
- Hybrid infrastructures: Third-party services from managed service providers (MSPs), combined cloud and on-premises networks
Security, reliability, and performance are key aspects of strong network infrastructure. You can use network taps and other devices to eliminate blind spots and enhance network security. Learn more about computer network infrastructure, different types of networks, and what you can do to enhance your network.
Benefits of Cultivating a Strong Network Infrastructure
Your network is at the heart of your business. But for it to function correctly, it needs the right support — in the form of effective network infrastructure. Now that we know what network infrastructure is, how can you ensure that you’re getting the most out of it?
In this digital age, an organization’s agility and productivity depend on more than just hardworking employees and excellent equipment. Running a smooth operation also requires a robust, clean, and secure network infrastructure. Without the right network infrastructure in place, you may suffer from poor user experience and security issues that can impact employee productivity, cost you money, and damage your brand.
As such, business executives must understand the importance of network infrastructure and be aware of the challenges and opportunities it presents. With this knowledge and the right tools in place, you are taking the first steps to ensure optimum productivity and help your organization maintain peak levels of performance.
Types of Network Infrastructure
There are various types of network infrastructure, including wired and wireless networks. There are also hybrid networks that use a combination of wired and wireless equipment. Let’s learn more about the different types of computer network infrastructure:
Wired
Wired network infrastructure uses physical wires to connect devices to the internet. These networks are more common in large organizations where speed and reliability are essential. Wired networks are also ideal in applications where large amounts of bandwidth are needed.
A wired network is often made up of a combination of Ethernet cables and fiber optic cables. Fiber optic cables offer lower latency and higher speeds, but they’re also more expensive.
You can connect physical network taps to a wired network by connecting a physical device to the cables to split the network. Physical network taps are easy to install. Once installed, monitoring ports in the network tap send out copies of the traffic for monitoring.
There are two types of network taps — passive and active. Passive taps don’t require a power source, which makes them reliable and easy to install. Active taps, on the other hand, do require a power source, meaning the tap won’t work in the event of a power outage.
Wired networks play a key role in network infrastructure services because they’re commonly used by large organizations. The sheer size of enterprise wired networks introduces new security and infrastructure challenges.
Wireless
Instead of using physical wires to transmit a signal to devices, a wireless network sends out wireless signals. Wireless networks are popular because they’re convenient and flexible. You don’t have to worry about running a cable to every device, so you have more options when you’re installing a wireless network.
There are different types of wireless technology. One of the latest innovations in wireless networks is 5G, the newest generation of wireless cellular networks. 5G offers improved performance over 3G and 4G, including faster speeds. This type of wireless connection is mostly used for smartphones, but you can set up a home 5G network too.
While wireless networks offer convenience, there are some drawbacks. If you’re trying to build a Zero Trust architecture, wireless networks are more challenging in terms of security. Wireless networks are also susceptible to interference and connectivity issues.
Hybrid
Today, many large organizations use a hybrid network that combines wireless and wired network infrastructure. These networks are common among large enterprises that need both wired and wireless connectivity.
Hybrid networks offer several benefits, but setting up a hybrid network is considerably more complex. The obstacles you face with a hybrid network may be unfamiliar.
If you can’t decide between the reliability and performance of wired networks or the convenience of wireless, a hybrid network infrastructure is a good middle ground.
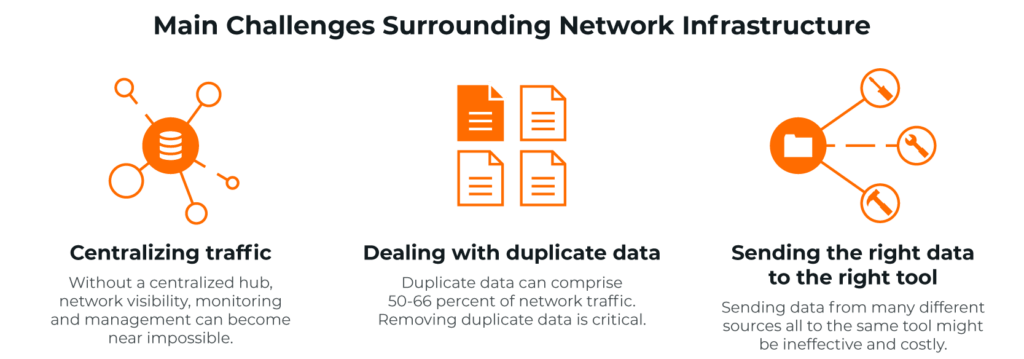
What Are the Main Challenges Surrounding Network Infrastructure?
There are several challenges involved with running a network infrastructure model. Some of the top network infrastructure challenges are:
- Centralizing traffic
- Dealing with duplicate data
- Sending the right data to the right tool
Boost Network Infrastructure with Gigamon
Keeping a clean and efficient network infrastructure is no small feat. That’s why it’s helpful to have a company with deep networking and security expertise on your side. Network infrastructures simply aren’t as cut and dried as they used to be; they are now often a mix of on-premises and cloud, including network infrastructure services. And even within on-premises networking, there tends to be a mishmash of different types of networks and vendors.
Inorganic growth and mergers and acquisitions can further muddle the network infrastructure. The result is that companies can end up with five separate tools that all monitor and manage one large hybrid network. For companies that want to keep their network safe and operating at peak performance, this is not ideal. Establishing one centralized hub for network visibility is critical and so is the ability to direct the right traffic to the right tools. That’s where Gigamon comes in.
The Gigamon Deep Observability Pipeline gives you complete network visibility, enhancing security and reliability. Traffic is aggregated and optimized before it’s sent to relevant security and monitoring tools, and you get full visibility into encrypted traffic. Gigamon can help you simplify your network and streamline network management. Request a free demo to see how Gigamon can help you boost your network infrastructure.
Further Reading
Featured Webinars
Hear from our experts on the latest trends and best practices to optimize your network visibility and analysis.

CONTINUE THE DISCUSSION
People are talking about this in the Gigamon Community’s Networking group.
Share your thoughts today







 Dan Daniels
Dan Daniels